Introduction to Histology: The Study of Tissues
What is Histology?
Histology is the study of tissues. The word is derived from the Greek words “histo” (tissue) and “logos” (study). Therefore, histology is the science of the microscopic structure of cells, tissues, and organs. Simply put, it's the study of tissues under a microscope.
This field examines the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues and is fundamental to understanding the structure and function of the entire body.
Why Health workers Need to Know Histology
A strong foundation in histology is not just for doctors or researchers; it is a critical component of a professional nurse's knowledge base. It elevates a nurse's practice from task-oriented care to a deeper, more analytical level of patient management.
Explains Form & Function
Shows how tissue structure relates to its job, making treatments like oxygen therapy more meaningful.
Identifies Disease
Knowing normal tissue helps nurses recognize changes in disease, aiding in assessments like wound care.
Enhances Practical Skills
Improves participation in collecting and interpreting lab samples (e.g., biopsies).
Informs Patient Education
Allows nurses to better explain conditions and treatments, leading to more informed care.
Medication Efficacy
Helps nurses anticipate medication effects and side effects by understanding drug-cell interactions.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Facilitates clearer communication with pathologists, doctors, and other healthcare professionals.
Methods of Histology
Histology employs various techniques to prepare tissues for microscopic examination. These methods are crucial for preserving tissue integrity and allowing for the study of their structure and function. The main steps involve tissue preparation, staining, and microscopy.
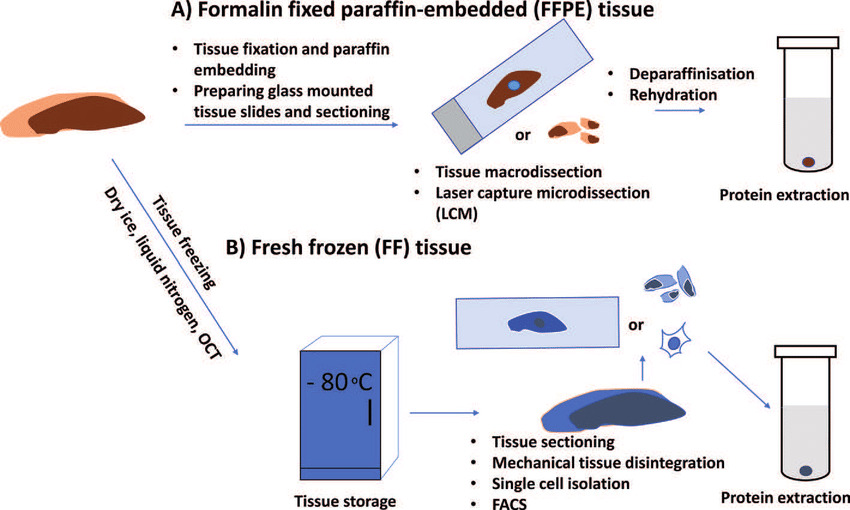
1. Tissue Preparation Techniques
This is the first and most critical step to preserve tissue and allow for thin sectioning. There are three main methods.
a. Paraffin Technique
This is the most common method for preparing tissues for routine histological examination.
Procedures of the Paraffin Technique:
- Tissue Sample Collection: Obtaining the sample (biopsy, surgical excision).
- Fixation: Preserving the tissue, commonly with 4% formaldehyde (formalin).
- Dehydration: Removing water with increasing concentrations of alcohol.
- Clearing: Replacing alcohol with a clearing agent like xylene.
- Impregnation: Infiltrating the tissue with melted soft paraffin.
- Embedding: Transferring the tissue to hard paraffin to form a solid block.
- Sectioning: Cutting the block into very thin (5-8 µm) sections using a microtome.
b. Celloidin Technique
Provides superior support for both soft and hard tissues, such as bones, teeth, and large brain sections.
Advantages:
- Excellent support for hard tissues
- Minimal shrinkage and distortion
- Good architectural preservation
Disadvantages:
- Very time-consuming process
- Difficult to cut very thin sections
- Requires specialized technical skills
c. Freezing Technique
Rapidly prepares tissues by freezing, especially for urgent diagnoses during surgery.
Advantages:
- Rapid diagnosis (minutes)
- Preserves molecules (DNA, RNA, proteins)
- Preserves antigens for immunostaining
Disadvantages:
- Poor staining and cellular detail
- Inadequate fixation compared to paraffin
- Expensive and complex equipment (cryostat)
2. Staining Techniques
Staining uses dyes to enhance the visibility of different tissue structures under the microscope. This is essential because most tissues are colorless.
Common Stains and Their Uses:
3. Microscopy Techniques
Microscopy is the use of microscopes to visualize small structures that are not visible to the naked eye.
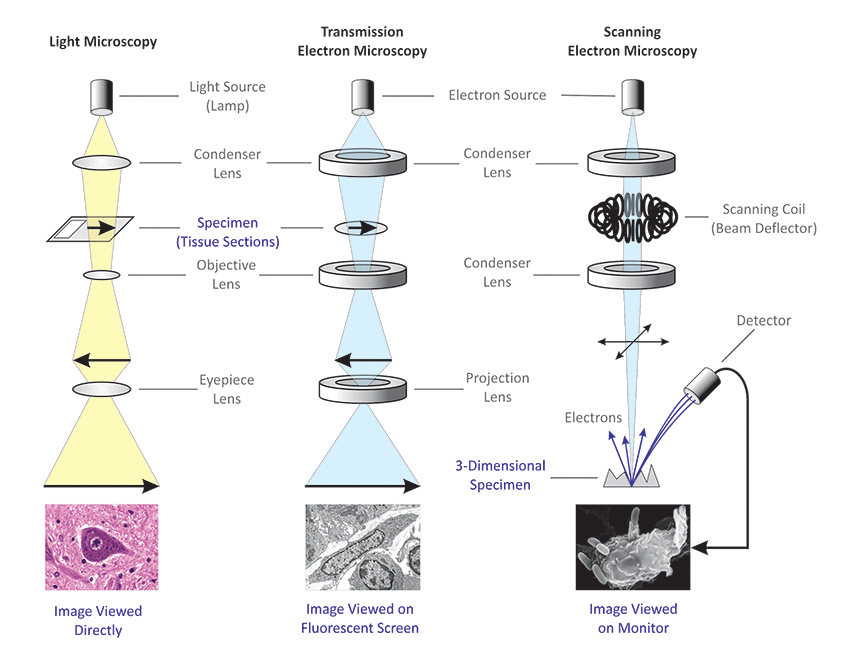
Light Microscope
Uses natural or electric light to examine stained sections. This is the most commonly used microscope in routine histology.
Electron Microscope
Uses a beam of electrons for much higher magnification. TEM provides high-resolution internal details, while SEM provides detailed 3D surface images.
Test Your Knowledge
Check your understanding of the concepts covered in this post.
1. Histology is defined as the study of:
- Cells under a light microscope.
- Gross anatomy of organs.
- Tissues under a microscope.
- Chemical composition of biological structures.
2. Why is understanding histology important for nurses regarding medication efficacy?
- It helps them prescribe the correct dosage.
- It allows them to understand how drugs interact with specific cell types and tissues.
- It teaches them how to administer intravenous medications.
- It explains the cost-effectiveness of different drugs.
3. Which tissue preparation technique is most commonly used for routine histological examination due to its preservation and hardening properties?
- Celloidin Technique
- Freezing Technique
- Paraffin Technique
- Vital Staining
4. What is the primary disadvantage of the Celloidin Technique mentioned in the text?
- It causes significant tissue shrinkage and distortion.
- It is a very rapid process.
- It is time-consuming and difficult to cut very thin sections.
- It poorly preserves hard tissues like bone.
5. In the Paraffin Technique, what is the purpose of the 'Clearing' step?
- To replace water with alcohol.
- To harden the tissue by coagulating proteins.
- To replace alcohol with a clearing agent like xylene.
- To embed the tissue in molten paraffin.
6. Which staining technique uses positively charged dyes to stain negatively charged cellular components, such as nuclei?
- Acidic Staining
- Basic Staining
- Neutral Staining
- Metachromatic Staining
7. Which stain is described as the "most routinely used" and provides a basic architectural overview of tissues, staining nuclei blue and cytoplasm pink?
- PAS (Periodic Acid-Schiff)
- Silver Stains
- Trichrome Stains
- Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E)
8. The Freezing Technique is particularly useful for:
- Ensuring minimal shrinkage over several days.
- Providing rapid diagnosis during surgical procedures.
- Creating very thin sections for routine examination.
- Hardening very delicate tissues like brain.
9. What is a key advantage of the Freezing Technique for molecular studies?
- It causes significant protein denaturation.
- It allows for rapid decomposition of cellular enzymes.
- It preserves biomolecules like DNA, RNA, and enzymes.
- It requires extensive prior chemical fixation.
10. Which type of electron microscope provides high-resolution images of the internal details of a specimen by passing electrons through it?
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- Light Microscope
- Cryostat
11. The Greek word "histo" in histology means ________________.
12. In the Paraffin Technique, ________________ is used to remove water from the tissue by immersing it in increasing concentrations of alcohol.
13. The primary fixative commonly used in the Paraffin Technique is ________________.
14. The technique that uses antibodies to show specific molecules or cell types, crucial for cancer diagnosis, is called ________________.
15. A cryostat is used to perform sectioning for the ________________ technique.
Quiz Complete!
Your Score:
0%
0 / 0 correct